Material Differentiation for Diagnosing Cardiovascular Disease: better visualization with SpectralDR technology
In a clinical diagnostic setting, the information provided by X-rays is crucial for identifying conditions such as cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, traditional X-rays face limitations due to obstructions from bone structures and medical devices when examining soft tissue. In many cases, visual indicators of heart disease may not be visible on standard X-rays because the ribs obscure a significant portion of the internal organs.
KA Imaging has developed the Reveal 35C with dual-energy X-ray technology to address these limitations. This innovative detector provides clear differentiation between bone and soft tissue in a single exposure, generating three distinct images: a soft tissue image, a bone image, and a standard X-ray image. Research shows that Reveal 35C has great potential to visualize underlying structures, including areas behind the ribs and heart, enhancing diagnostic confidence in complex cases.
Coronary Calcifications: helping the early-identification of higher-risk patients
Currently, cardiac CTs used to identify coronary artery calcifications are the best indicator for predicting future cardiac events. Dual-energy X-ray technology can provide a lower cost, lower radiation early-stage option.
A recent study published in the Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal examined the effectiveness of the Reveal 35C’s dual-energy X-ray in assessing coronary risks. The findings revealed that this technology significantly enhances the accurate diagnosis of coronary artery calcifications (CAC), used as an indicator of cardiovascular disease.
In this study, researchers observed 61 bone marrow transplant patients selected for their higher cardiac complication risk. Each patient received a dual-energy chest X-ray in posteroanterior and lateral projections, as well as a low-dose chest CT. Two experienced radiologists independently assessed the images. Results showed that dual-energy imaging detected CAC with higher diagnostic confidence than the traditional X-ray.
According to the study authors, “The single-exposure, dual-energy chest X-ray has shown improved detection of both calcium deposits in the heart’s arteries, as well as valve and vascular calcifications – both indicators of a higher risk for heart disease – when compared to conventional X-ray imaging.” They suggest that “the initial X-ray finding may help clinicians with assessing risk earlier, and guide additional testing if clinically warranted, all leading to improved risk management for patients at risk of heart disease and/or a cardiac event.”
Learn more about the results of Reveal 35C’s study
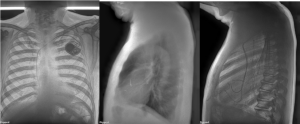
Posteroanterior (PA) bone dual-energy image (left), lateral soft tissue dual-energy image (middle), and lateral bone dual-energy image (right) using the Reveal 35C highlighting the presence of coronary calcifications that is not readily visible in the conventional radiograph images.
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of cardiovascular disease and its manifestations on imaging can significantly enhance patient outcomes. Accurate identification facilitates early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early detection remains key, and the collaborative efforts of patients and healthcare providers can lead to improved heart health and quality of life. As companies like KA Imaging seek to innovate the X-ray technology used for CXR, doctors are working to reduce the impact of cardiovascular disease on their patients and the burden on the healthcare system.
Improve the visualization of Cardiac Calcifications with Reveal 35C
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease in Radiology
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a broad term that encompasses various heart and blood vessel disorders, including heart attacks, heart failure, arrhythmias, and hypertension. Understanding how these conditions manifest on X-ray is crucial for effective diagnosis and management. This article will dive into the ways clinicians identify cardiovascular diseases through X-rays, the signs and symptoms patients should monitor, the testing process, and the diagnostic imaging techniques used.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Cardiovascular Disease?
Doctors begin by gathering comprehensive patient histories and asking about symptoms. Key symptoms of cardiovascular issues include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or wheezing
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Poor blood supply
- Fatigue
- Episodes of a fast or uneven heartbeat (palpitations)
Once doctors gather information about the patient’s symptoms, they confirm their diagnoses through a combination of blood tests, heart monitoring, and various imaging tests. These are the most common tests for CVD.
Blood tests can reveal levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, and markers of inflammation or heart damage. They also assess kidney function and electrolyte levels, which are critical to heart health.
Heart monitoring, including electrocardiograms (ECGs) and Holter monitors, provides valuable information about heart rhythm and electrical activity. These methods help detect arrhythmias and other abnormalities that suggest underlying cardiovascular disease.
Imaging The Heart: How It Works
Imaging plays a fundamental role in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases. Physicians often order chest X-rays (CXRs) to gain insights into a patient’s heart and lung structures. A CXR evaluates the chest bones, heart, and lungs. It also confirms the proper placement of pacemakers, defibrillators, and other cardiac devices.
CXRs can diagnose various potential cardiovascular issues, such as:
- Fluid accumulation in or around the lungs
- An enlarged heart
- Blood vessel abnormalities
- Congenital cardiovascular diseases
- Calcium buildup within the heart or blood vessels.
Each of these indicators can signify underlying cardiovascular problems that warrant further investigation.
How Does CXR Show Cardiovascular Disease?
A chest X-ray provides images of the external structures of the heart, rather than its internal components. This means that while a CXR does locate signs of heart failure or cardiomegaly, it cannot reveal internal mechanisms, such as valve function or chamber architecture. Nevertheless, several key indicators of cardiovascular disease can appear externally on a CXR:
- Pulmonary Venous Congestion: This condition occurs when the volume of blood in the upper lungs exceeds that in the lower lungs, often due to heart failure. The distribution of blood is observed via chest X-ray. The upper zone blood vessels appear bigger than the lower zone vessels, showing uneven distribution. When the blood vessels are enlarged, they appear hazy, and the outline is hard to identify.
- Cardiomegaly: Enlarged hearts indicate heart failure or other conditions. Cardiomegaly is characterized by an increase in heart size, an essential aspect that a CXR can reveal. Doctors will compare the CXR of a healthy patient to the patient with cardiovascular disease to understand the size difference.
- Kerley B Lines: These lines are seen on a chest X-ray and represent swollen interlobular septa within the lungs. They appear as horizontal lines extending to the pleural surface. It’s a sign of interstitial edema and heart failure.
- Alveolar Edema: When the heart fails to effectively pump blood through the body, Alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs, become filled with fluid. This is because the blood vessels responsible for transporting blood to the lungs are backed up. The condition is known as alveolar edema. The fluid is visible in chest X-rays.
- Pleural Effusions: Excess fluid found between the pleura layers (the space between the lung and the chest wall) can be identified on a CXR. Like alveolar edema, it happens because of backed up blood vessels. It is a sign of heart disease, but it’s also caused by pneumonia, kidney disease, and liver disease.
Ultimately, advancing our understanding of cardiovascular disease and its imaging manifestations is essential to improving patient outcomes. Early and accurate detection enables timely intervention and more effective treatment. With ongoing innovation in X-ray technology, healthcare providers are better equipped to combat cardiovascular disease, reduce its impact on patients, and alleviate strain on healthcare systems worldwide.
