In biomedical research, advanced imaging technologies are essential for uncovering microstructural changes in tissues, tracking disease progression, and evaluating therapeutic outcomes. The ability to visualize and differentiate soft biological materials—without damaging the sample—can accelerate both discovery and translational research.
The inCiTe Family of Microscopes, developed by KA Imaging, delivers this capability through a unique combination of high-resolution 3D imaging, propagation-based phase contrast, and—for the first time in a benchtop micro-CT system—dual-energy spectral imaging. These features allow researchers to non-invasively capture internal biological structures and differentiate materials based on composition and density—all within a single scan.
This article delves into the capabilities of the inCiTe microscopes and highlights their transformative impact on a number of biomedical research studies.
Introducing The inCiTe Family of Microscopes
The inCiTe Family of Microscopes were developed by KA Imaging, a spin-off of the University of Waterloo. KA Imaging has a history of advancing the world of X-ray imaging with innovative technology and unique capabilities. The inCite 3D microscope being a prime example of their state-of-the-art NDT and research technologies:
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope: KA Imaging’s benchtop CT system designed for high-detail imaging of low-density materials. With its superior phase contrast technology, the inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope accurately captures low-density materials with weak X-ray absorption.
- BrillianSe™ X-ray Detector: A patented direct-conversion detector at the core of the inCiTe systems. Utilizing an amorphous selenium (a-Se) photoconductor and CMOS readout, it directly converts X-ray photons into electrical signals—eliminating optical scatter and reducing noise for superior image fidelity. BrillianSe™ is also available for custom micro-CT applications.
- inCiTe 2.0 3D X-ray Microscope: Building on the original inCiTe, this next-generation system combines high-resolution phase contrast with dual-energy spectral imaging. When paired with KA Imaging’s Reveal detector, inCiTe 2.0 captures dual-energy data in a single scan, enabling researchers to differentiate and visualize biological materials with sub-micron resolution and material-specific contrast.
Core inCiTe Microscope Features for Biomedical Research
- Non-destructive: inCiTe can analyze samples in fine detail without damaging or destroying them. In biomedical research, if researchers want to study a sample multiple times over a long period, maintaining the integrity of the sample is crucial. Additionally, this type of non-destructive testing keeps the sample from being altered over time, leading to a longer sample lifespan and more accurate results.
- High-Resolution 3D Imaging: By using VGSTUDIO MAX from Volume Graphics, you can reconstruct images taken by an inCiTe microscope slice by slice. This can be used to visualize biological microstructures, which often have complex geometries hard to depict in 2D imaging.
- Material and Density Differentiation: Research is simplified when an X-ray image can demonstrate differences between tissues, allowing researchers to identify one organ from another. This is typically achieved with high resolution, contrast, and spectral imaging — key features of the inCiTe 2.0 microscope. Moreover, being able to track density can help identify changes in biological tissue. This is important for analyzing how body tissue changes (ex. becoming inflamed, growing larger) from the effect of a disease or treatment.
- No Sample Preparation Required: Unlike many imaging techniques that require staining, sectioning, or contrast agents, inCiTe operates without sample prep. This streamlines workflows, reduces potential handling artifacts, saves researchers time, and lowers overall lab operational costs.
inCiTe vs. SEM for Biomedical Tissue Imaging
inCiTe excels in non-destructive, high-contrast imaging of intact biological samples, especially soft tissues that are challenging for SEM. While SEM offers ultra-high surface resolution, it falls short for internal structure visualization, live tissue monitoring, or multi-use sample handling. Check the comparison below:
Features
- Sample Preparation
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- None required — no staining, slicing, or coating
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Extensive prep — dehydration, fixation, coating needed
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Non-Destructive Imaging
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- ✅ Yes — preserves sample for longitudinal studies
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- ❌ No — samples are often altered or destroyed
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Imaging Low-Density Tissues
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Excellent — phase contrast highlights soft tissue
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Poor — limited contrast for soft, non-conductive tissue
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- 3D Imaging Capability
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Built-in 3D volume reconstruction (micro-CT)
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Not native — SEM is surface/topography imaging
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Field of View
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Large — up to 30 mm diameter (inCiTe 2.0)
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Small — typically < 1 mm without stage stitching
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Resolution
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Down to 0.8 µm voxels at max magnification
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Higher surface resolution — down to nm range
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Spectral Imaging Capability
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- ✅ Yes (inCiTe 2.0) — dual-energy data in single scan
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- ❌ No — cannot differentiate materials by composition
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Throughput / Scan Time
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Fast setup, no prep → high throughput
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Slower due to sample prep and alignment
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Suitability for Biological Samples
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Ideal for soft tissues, implants, organs, etc.
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Best for hard, dry, conductive materials
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Destructive Risk
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- None — full sample recovery
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- High — especially for delicate or hydrated tissues
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Lab Workflow Fit
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
- Plug-and-play; scan in < 20 minutes from power-on
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Requires skilled operator and specialized facilities
- inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope
inCiTe In Action: Biomedical Research Applications
Bone and Orthopedic Studies with University of Waterloo
The inCiTe 3D Microscope was recently picked up by University of Waterloo to be utilized in some of their biological research projects. These projects will be led by Dr. Stewart McLachlin and Dr. Naveen Chandrashekar in the Orthopaedic Mechatronics Laboratory. University of Waterloo will be the first in Canada to use KA Imaging’s innovative inCiTe 3D microscope for their research studies. Their goal is to make new discoveries that will lead to better orthopedic treatment.
Using the inCiTe 3D microscope, the researchers will be able to conduct an in-depth study of bone and joint tissue — something that wasn’t possible with traditional CT imaging systems due to the tissues’ low density. With inCiTe’s superior phase contrast technology, the contrast and resolution possible with these samples is expanding significantly. Researchers will be able to see inside the biological tissues and see how the internal microstructure is formed and altered in different scenarios.
Research and Knowledge Transfer with University of Greenwich
In 2023, KA Imaging partnered with University of Greenwich in the UK to perform more biological research studies with the inCiTe 3D microscope. Being the first of its kind in Europe, inCiTe’s phase contrast technology will make it possible for Professor Gianluca Tozzi and his research team to study biological tissue with low X-ray absorption.
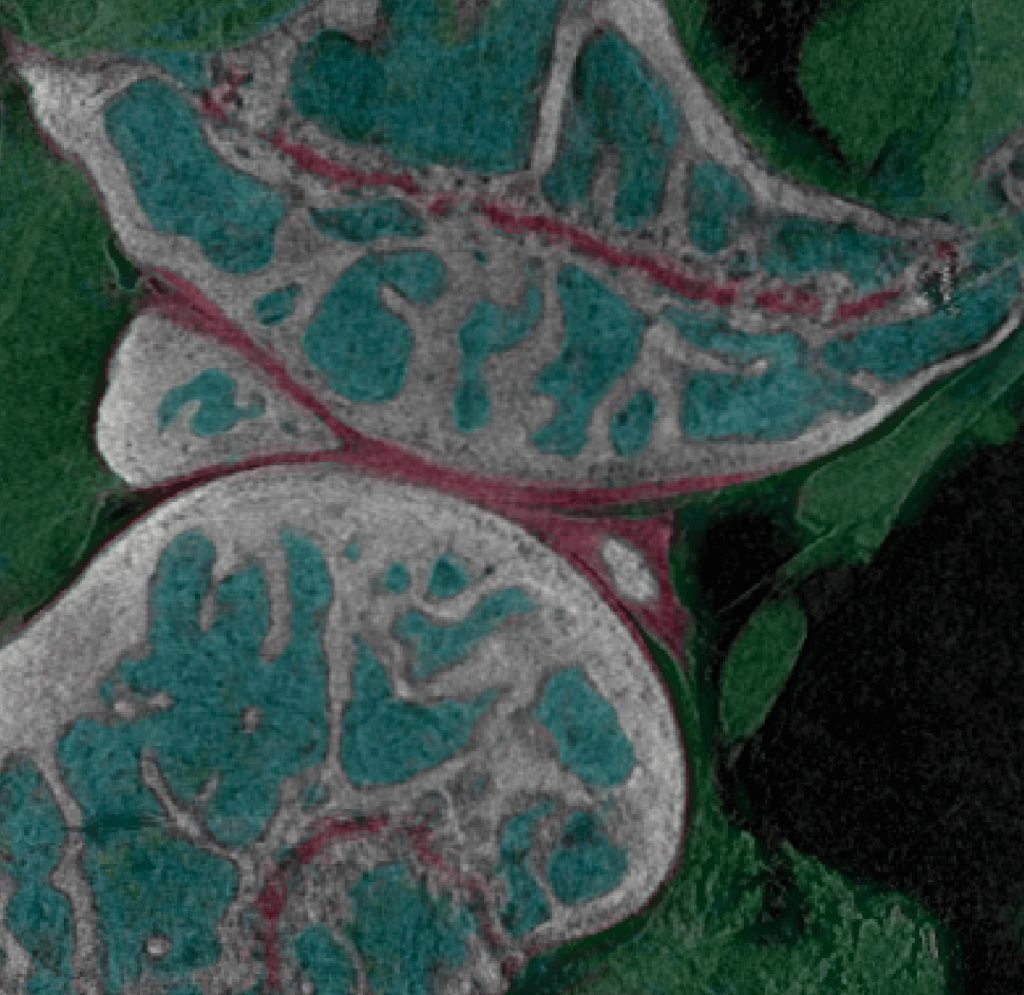
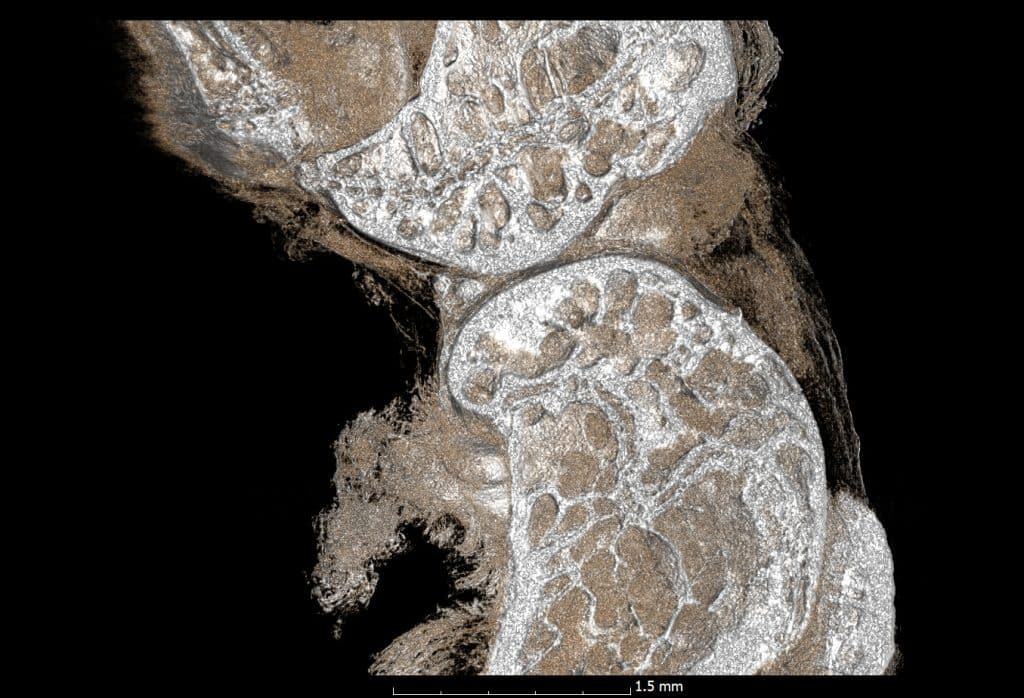
InCiTe in Action: Images of Biological Tissue Under a 3D X-ray Microscope
Below are two images of biological tissue captured by the inCiTe 3D X-ray Microscope. On the left is an image of a biological sample studied by University of Greenwich as part of their partnership with KA Imaging. On the right is a high-detail image of a mouse knee captured by inCiTe.