How KA Imaging’s Dual-energy Solution Sets a New Industry Standard
KA Imaging, Reveal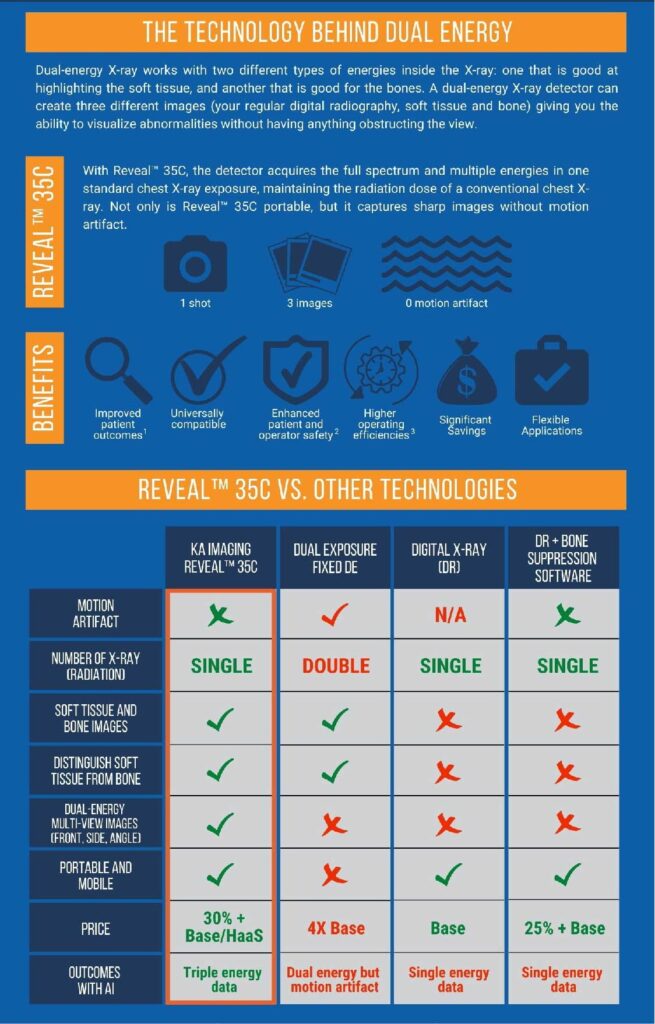
Reveal™ 35C is available in Canada and the USA. Contact us for inquiries and availability in other countries.
Reveal™ 35C is the world’s first and only single exposure, portable, digital dual-energy subtraction (DES) X-ray detector that overcomes previous DES technical limitations. This detector raised the possibility of a DES retrofit in existing digital X-ray rooms. The portability of a single exposure DES detector also allows for point-of-care high-quality diagnostic imaging to increase access in underserved regions and low mobility patients.
Dual-energy has been proven to detect more solitary pulmonary nodules, pneumothorax, pneumonia, tuberculosis, and coronary calcium than conventional analog or digital chest X-rays. This early detection enables faster/improved patient outcomes, additional hospital revenue, cost savings to healthcare systems, and reduces exposure to malpractice claims. Additionally, the Reveal™ 35C has 20X less radiation compared to CT scans and reduces radiologist reading time for X-rays by 30% at 10X lower purchase and operating costs than traditional CT scans.
VISIT THE PRODUCT PAGE
References
1. Improved patient outcomes
(Lung Nodules) Oda, Seitaro, Kazuo Awai, Yoshinori Funama, Daisuke Utsunomiya, Yumi Yanaga, Koichi Kawanaka, Takeshi Nakaura et al. “Detection of small pulmonary nodules on chest radiographs: efficacy of dual-energy subtraction technique using flat-panel detector chest radiography.” Clinical radiology 65, no. 8 (2010): 609-615.
(Pneumothorax) Urbaneja, A., Dodin, G., Hoosu, G., et al. (2018) Added Value of Bone Subtraction in Dual-energy Digital Radiography in the Detection of Pneuomothorax: Impact of Reader Expertise and Medical Specialty. The Association of University Radiologists. Elsevier Inc.
(Pneumonia) Martini, Katharina, Marco Baessler, Stephan Baumueller, and Thomas Frauenfelder. “Diagnostic accuracy and added value of dual-energy subtraction radiography compared to standard conventional radiography using computed tomography as standard of reference.” PloS one 12, no. 3 (2017): e0174285.
(Tuberculosis) Sharma, Madhurima, Manavjit Singh Sandhu, Ujjwal Gorsi, Dheeraj Gupta, and Niranjan Khandelwal. “Role of digital tomosynthesis and dual energy subtraction digital radiography in detection of parenchymal lesions in active pulmonary tuberculosis.” European Journal of Radiology 84, no. 9 (2015): 1820-1827.
(Coronary Calcifications) Song, Yingnan, Hao Wu, Di Wen, Bo Zhu, Philipp Graner, Leslie Ciancibello, Haran Rajeswaran et al. “Detection of coronary calcifications with dual energy chest X-rays: clinical evaluation.” The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging (2020): 1-8.
Kuhlman, Janet E., Jannette Collins, Gregory N. Brooks, Donald R. Yandow, and Lynn S. Broderick. “Dual-energy subtraction chest radiography: what to look for beyond calcified nodules.” Radiographics 26, no. 1 (2006): 79-92.
2. Enhanced patient and operator safety.
Kuhlman, Janet E., Jannette Collins, Gregory N. Brooks, Donald R. Yandow, and Lynn S. Broderick. “Dual-energy subtraction chest radiography: what to look for beyond calcified nodules.” Radiographics 26, no. 1 (2006): 79-92.
3. Higher operating efficiencies
Manji, Farheen, Jiheng Wang, Geoff Norman, Zhou Wang, and David Koff. “Comparison of dual energy subtraction chest radiography and traditional chest X-rays in the detection of pulmonary nodules.” Quantitative imaging in medicine and surgery 6, no. 1 (2016): 1.
